Biography
Personal Pronouns: He/Him
Contact details:
- +44 (0) 1603 450 068
Mark McMullan is an evolutionary biologist with a track-record in host-pathogen co-evolution and a specific focus on crop domestication and pathogen invasion.
He uses evolutionary biology and population genetics, molecular dating, recombination analyses, and individual based modelling to understand the role of adaptation in pathogen emergence and invasion, as well as host response.
Mark is particularly interested in harnessing diversity in genetic reservoirs to understand host-pathogen co-evolution. He is developing these ideas in two systems, wheat take-all, the most important root disease of wheat worldwide, and sugar beet rust, shared between both the crop and the wild crop relative.
Take-all of wheat has been an understudied disease and the team have recently delivered a UK pangenome for the fungus as well as using novel methods to explore associations between repetitive DNA and virulence.
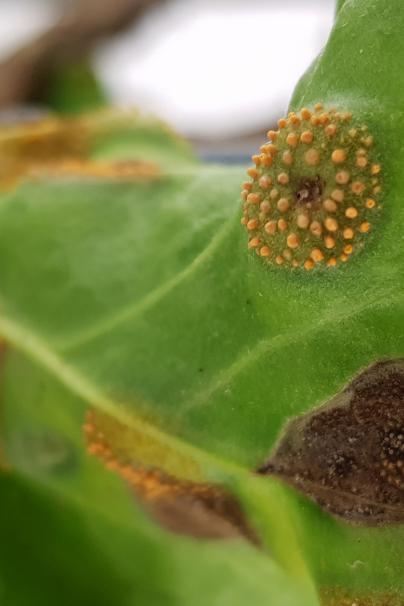
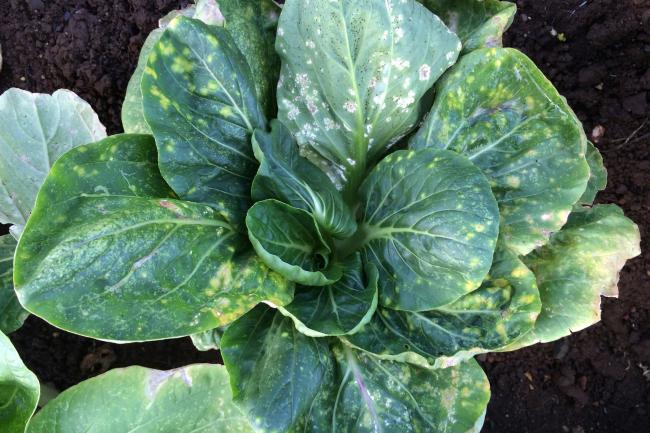
In sugar beet Mark is working on both host and pathogen, on the host using direct wild association genetics and population genetics to identify novel resistance genes, as well as identifying pathogen diversity associated with success on the sugar beet crop.
Mark aims to understand the evolutionarily ingredients for invasion, while at the same time identifying native hosts that are already resistant to those pathogens.